n°49 — Lawrence Weiner: We Are Ships at Sea, Not Ducks On a Pond. Author: Joris Kritis with interviews with Nora Turato & Linda van Deursen
Authors: Joris Kritis + interviews with Linda van Deursen and Nora Turato
62 pages (44 pages A4 + 16 pages A5)
21 × 29,7 cm, CMYK + 1 PMS on Cover
January 2025
ISBN: 979-10-95991-48-8
ISSN: 2558-2062
Lawrence Weiner’s use of graphic design has always been of fascination for graphic designers. ‘What makes Weiner’s work seductive to graphic designers is his resolutely non-apologetic method of displaying words without need for any explanation.’* But in this text a comparative analysis is made of different voices about Weiner’s use of graphics & typography.
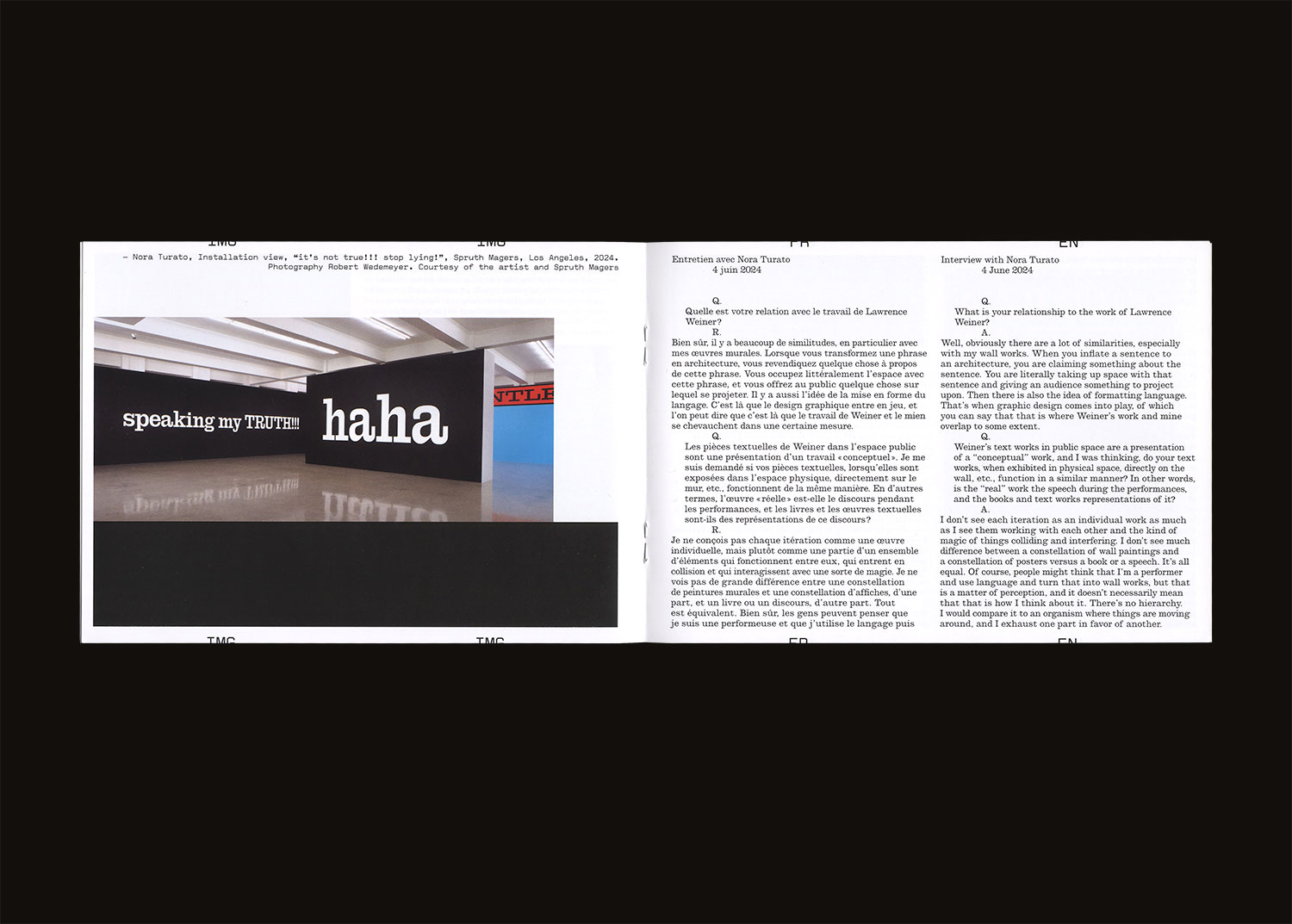
Next to a speculative history of Weiner’s formal language, two interviews—with graphic designer Linda Van Deursen and artist Nora Turato—pay attention to Weiner’s enduring legacy.
*— Russel Holmes, “The Work Must Be Read”, Eye Magazine, Autumn, 1998, https://www.eyemagazine.com/feature/article/the-work-must-be-read.